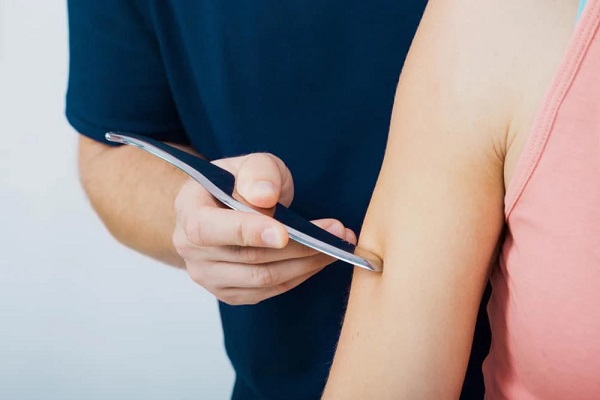
Supraspinatus tendonitis, also known as supraspinatus tendinopathy, is a common issue among individuals over 30, particularly those engaging in activities requiring repetitive overhead arm movements. Join the Vung Tau Shoulder Pain Therapy Center to learn more about this condition!
Structure and Function of the Supraspinatus Tendon
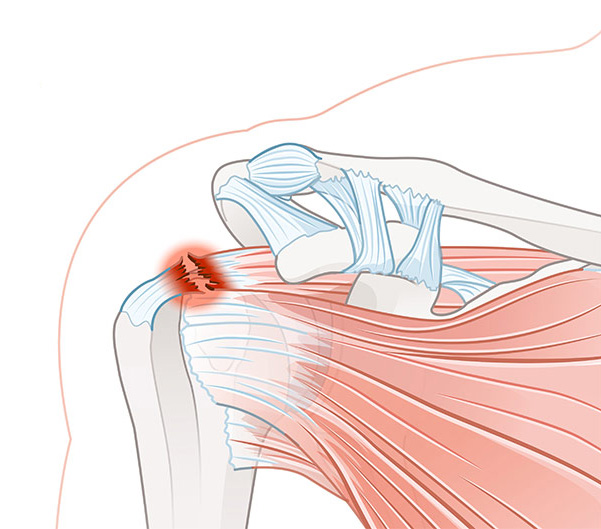
The supraspinatus tendon, part of the rotator cuff, works alongside the infraspinatus, subscapularis, and teres minor muscles, as well as associated muscles like the deltoid, sternocleidomastoid, and pectoralis major. These structures play a critical role in maintaining the stability and balance of the humerus on the scapula during overhead arm movements. The supraspinatus tendon lies beneath the acromion and endures the greatest stress during shoulder motion, making it more susceptible to injury compared to other rotator cuff muscles.
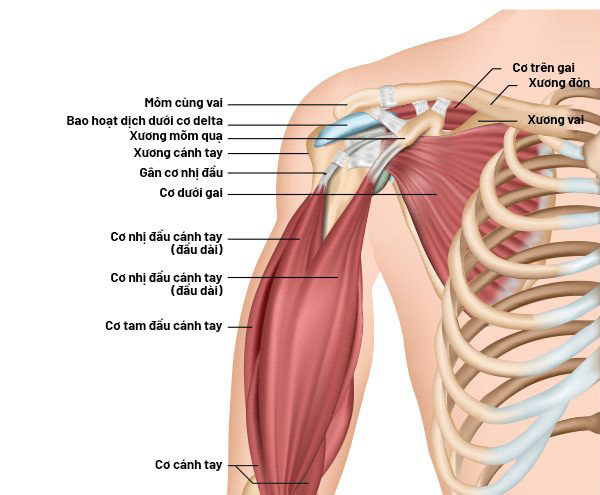
What is Supraspinatus Tendonitis?
Supraspinatus tendonitis, or shoulder tendinopathy, is characterized by inflammation and swelling around the shoulder joint, typically following shoulder muscle injury. This condition is prevalent in individuals over 30 and causes pain at the site of inflammation when reaching backward or raising the shoulder above the head. It is also considered a degenerative process of the shoulder muscles due to injury. Shoulder function declines as the cartilage wears down due to tendon inflammation.
The shoulder joint is stabilized by the rotator cuff, also known as the biceps tendon, which connects the humerus to the scapula. The rotator cuff is crucial for supporting and rotating the arm. In supraspinatus tendonitis, the tendons within the rotator cuff thicken, causing pain and hindering shoulder movement.
Causes of Supraspinatus Tendonitis
Supraspinatus tendonitis is common among athletes participating in sports involving repetitive overhead motions, such as badminton, table tennis, volleyball, or swimming. Other risk factors include anatomical variations in the shoulder joint, imbalances or dysfunctions in scapular motion, and aging.
The risk is also higher in individuals with chronic conditions like diabetes, dyslipidemia, or obesity. Preliminary evidence suggests that genetic factors may also contribute to an increased risk of supraspinatus tendonitis.
Even individuals who do not participate in sports may develop shoulder tendonitis if the shoulder is injured due to impact or excessive strain.
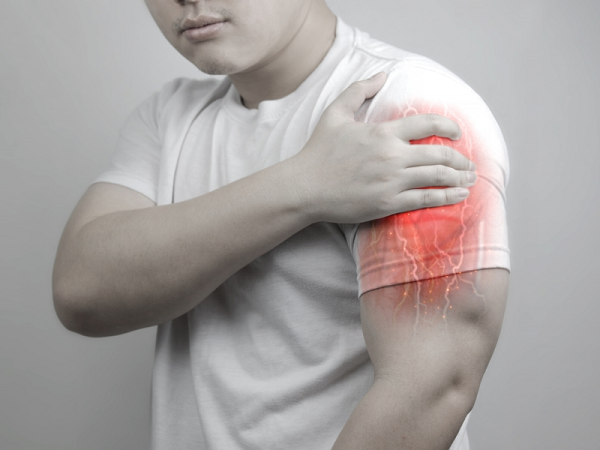
Common Symptoms of Supraspinatus Tendonitis
Individuals with supraspinatus tendonitis often experience pain during overhead arm movements or daily activities such as reaching for objects, combing hair, or dressing. Clinical signs include abnormal shoulder pain and stiffness, particularly during activity or upon touch. Symptoms of supraspinatus tendonitis include:
- Shoulder stiffness
- Pain in the anterior shoulder and arm when raising the scapula
- Clicking sounds in the shoulder during movement
- Tenderness and mild swelling at the inflamed tendon site
- Pain during arm movement
- Intense pain that disrupts sleep
- Significant shoulder weakness, with severe cases leading to loss of shoulder mobility
Diagnosis of Supraspinatus Tendonitis
Diagnosis involves patients performing specific movements using tests like the Hawkins-Kennedy or Jobe’s Test. Imaging techniques may also be used, including:
-
- Ultrasound: Provides the clearest imaging of soft tissues, ideal for assessing the condition of shoulder tendons and muscles.
- X-ray: Reveals the position and structure of internal tissues and bones, identifying small bone spurs or tendon calcification.
- MRI: Uses magnets and radio waves to detect inflammation, fluid accumulation, tendon tears, or degeneration in the shoulder.
Non-Pharmacological Physical Therapy
For mild pain, supraspinatus tendonitis can be successfully treated with rehabilitation exercises combined with rest. The Graston myofascial release technique, combined with ultrasound therapy to reduce inflammation, is currently the most effective non-invasive treatment, eliminating the need for glucocorticoid injections or medications.
During the treatment phase, myofascial release helps prevent rotator cuff muscle stiffness, reduces pressure on the scapular region, and gradually alleviates swelling at the inflamed site. Simultaneously, ultrasound therapy targets inflammation in parallel with muscle treatment. After 5–7 weeks of therapy, depending on individual response, pain typically reduces by 70–80%, and patients transition to the recovery phase.
In the recovery phase, patients perform prescribed exercises under guidance, with exercise intensity gradually increasing. Patients can return to work and sports once they achieve optimal range of motion, restored muscle strength, and shoulder joint stability.
Recovery duration varies based on age, treatment response, exercise effort, and the type of sport. Recovery timelines for supraspinatus tendonitis patients include:
- Badminton: 8–10 weeks
- Recreational volleyball: 8–10 weeks
- Professional volleyball: 12–16 weeks
- Tennis: 10–12 weeks
- Baseball: 12–16 weeks
- Javelin throwing: 8–10 weeks
- Bench press: 12–16 weeks
- Swimming: 5 months or more
Myofascial release physical therapy is a long-term treatment combining physical therapy with targeted exercises. Patients must remain consistent and follow the prescribed treatment schedule. Andora Physical Therapy Clinic is a leading rehabilitation and physical therapy center in Vung Tau. Our physical therapy methods are tailored flexibly to suit each patient’s pain condition and unique physiology.
Free consultation and condition assessment at Andora Orthopedic Clinic:
- Address: 123 Truong Cong Dinh, Vung Tau Ward, HCM City
- WhatsApp/Viber: (+84)87724 7272
- Facebook | X (Twitter) | Tiktok
Learn more about Musculoskeletal Disorders and Nutrition plans to effectively care for and restore musculoskeletal health.